Categories :-Introduction to WCF , Differences Between WCF and ASP.NET Web Services
Introduction :-
Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) is an SDK for developing and deploying services on Windows. WCF provides a runtime environment for your services, enabling you to expose CLR types as services, and to consume other services as CLR types. In this article, I am going to explain how to implement restful service API using WCF 4.0 . The Created API returns XML and JSON data using WCF attributes.
REST uses some common HTTP methods to insert/delete/update/retrieve information which is below:
- GET - Requests a specific representation of a resource
- PUT - Creates or updates a resource with the supplied representation
- DELETE - Deletes the specified resource
- POST - Submits data to be processed by the identified resource
Q.Why and Where to Use REST?
- Less overhead (no SOAP envelope to wrap every call in)
- Less duplication (HTTP already represents operations like
DELETE,PUT,GET, etc. that have to otherwise be represented in a SOAP envelope). - More standardized - HTTP operations are well understood and operate consistently. Some SOAP implementations can get finicky.
- More human readable and testable (harder to test SOAP with just a browser).
- Don't need to use XML (well, you kind of don't have to for SOAP either but it hardly makes sense since you're already doing parsing of the envelope).
- Libraries have made SOAP (kind of) easy. But you are abstracting away a lot of redundancy underneath as I have noted. Yes, in theory, SOAP can go over other transports so as to avoid riding atop a layer doing similar things, but in reality just about all SOAP work you'll ever do is over HTTP.
Q.Step by Step Guide For Develop WCF restful web service
We will develop Restful WCS API in 6 steps. So let’s start now.
STEP 1
First of all launch Visual Studio 2010. Click FILE->NEW->PROJECT. Create new "WCF Service Application".
STEP 2
Once you create the project, you can see in solution that By Default
WCF service and interface file are already created. Delete By default
created file as we will create our own interface and WCF service file.
STEP 3
Now right click on solution and create one new WCF service file. I have given name to the service file as “RestServiceImpl.svc”.
STEP 4
As I explained at the start of the article that we will be writing an
API which can return data in XML and JSON format, here is the interface
for that. In
IRestServiceImpl, add the following code:Copy the Above shource Code as shown Below
| [ServiceContract] public interface IRestServiceImpl { [OperationContract] [System.ServiceModel.Web.WebInvoke(Method = "GET",ResponseFormat=System.ServiceModel.Web.WebMessageFormat.Xml, BodyStyle =System.ServiceModel.Web.WebMessageBodyStyle.Wrapped, UriTemplate = "xml/{id}")] string XMLData(string id); [OperationContract] [System.ServiceModel.Web.WebInvoke(Method = "GET", ResponseFormat = System.ServiceModel.Web.WebMessageFormat.Json, BodyStyle = System.ServiceModel.Web.WebMessageBodyStyle.Wrapped, UriTemplate = "json/{id}")] string JSONData(string id); } |
In the above code, you can see two different methods of
IRestService which are XMLData and JSONData. XMLData returns result in XML whereas JSONData in JSON. STEP 5
Open the file RestServiceImpl.svc.cs and write the following code over there:
Find the Source as shown below
| public class RestServiceImpl : IRestServiceImpl { #region IRestService Members public string XMLData(string id) { return "You Request Porduct" + ":"+id; } public string JSONData(string id) { return "Yor Request Product" +":"+ id; } #endregion } |
STEP 6
Now let’s move to configuration part which is the last one. There
will be two basic parts of the configurations file which we must have to
understand.
<services>
This part contains information about the End Point. Below are the code details.
<behaviors>
This part contains details about service and endpoint behavior.Source code of web.config file as shown below
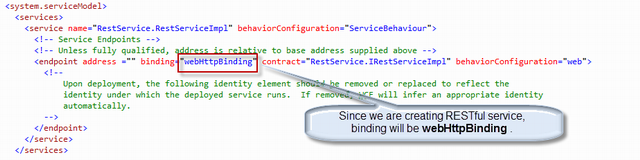
| <?xml version="1.0"?> <configuration> <system.web> <compilation debug="true" targetFramework="4.0" /> </system.web> <system.serviceModel> <services> <service name="RestService.RestServiceImpl" behaviorConfiguration="metadataBehavior"> <endpoint address="" binding="webHttpBinding" contract="RestService.IRestServiceImpl" behaviorConfiguration="web"> </endpoint> </service> </services> <behaviors> <serviceBehaviors> <behavior name="metadataBehavior"> <!-- To avoid disclosing metadata information, set the value below to false and remove the metadata endpoint above before deployment --> <serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled="true"/> <!-- To receive exception details in faults for debugging purposes, set the value below to true. Set to false before deployment to avoid disclosing exception information --> <serviceDebug includeExceptionDetailInFaults="false"/> </behavior> </serviceBehaviors> <endpointBehaviors> <behavior name="web"> <webHttp/> </behavior> </endpointBehaviors> </behaviors> <serviceHostingEnvironment multipleSiteBindingsEnabled="true" /> </system.serviceModel> <system.webServer> <modules runAllManagedModulesForAllRequests="true"/> </system.webServer> </configuration> |
Build your Project Which Shown Below
You got -: Service added Succefully in bottom of left hand site of the corner
Output
In xml and json format as shown below
Xml Format
Xml Format
JSON Format
1. What is the difference between WCF and ASMX Web Services?
Simple and basic difference is that ASMX or ASP.NET web service is
designed to send and receive messages using SOAP over HTTP only. While
WCF can exchange messages using any format (SOAP is default) over any
transport protocol (HTTP, TCP/IP, MSMQ, NamedPipes etc).
Another tutorial WCF Vs ASMX has detailed discussion on it.
2. What are WCF Service Endpoints? Explain.
For Windows Communication Foundation services to be
consumed, it’s necessary that it must be exposed; Clients need
information about service to communicate with it. This is where service
endpoints play their role.
A WCF service endpoint has three basic elements i.e. Address, Binding and Contract.
- Address: It defines "WHERE". Address is the URL that identifies the location of the service.
- Binding: It defines "HOW". Binding defines how the service can be accessed.
- Contract: It defines "WHAT". Contract identifies what is exposed by the service.
3. What are the possible ways of hosting a WCF service? Explain.
For a Windows Communication Foundation service to
host, we need at least a managed process, a ServiceHost instance and an
Endpoint configured. Possible approaches for hosting a service are:
- Hosting in a Managed Application/ Self Hosting
- Console Application
- Windows Application
- Windows Service
- Hosting on Web Server
- IIS 6.0 (ASP.NET Application supports only HTTP)
- Windows Process Activation Service (WAS) i.e. IIS 7.0 supports HTTP, TCP, NamedPipes, MSMQ.
4. How we can achieve Operation Overloading while exposing WCF Services?
By default, WSDL doesn’t support operation overloading. Overloading
behavior can be achieved by using "Name" property of OperationContract
attribute.
[ServiceContract]
interface IMyCalculator
{
[OperationContract(Name = "SumInt")]
int Sum(int arg1,int arg2);
[OperationContract(Name = "SumDouble")]
double Sum(double arg1,double arg2);
}
When the proxy will be generated for these operations, it will have 2 methods with different names i.e. SumInt and SumDouble.
5. What Message Exchange Patterns (MEPs) supported by WCF? Explain each of them briefly.
1. Request/Response
2. One Way
3. Duplex
Request/Response
It’s the default pattern. In this pattern, a response message will
always be generated to consumer when the operation is called, even with
the void return type. In this scenario, response will have empty SOAP
body.
One Way
In some cases, we are interested to send a message to service in
order to execute certain business functionality but not interested in
receiving anything back. OneWay MEP will work in such scenarios.
If we want queued message delivery, OneWay is the only available option.
Duplex
The Duplex MEP is basically a two-way message channel. In some cases,
we want to send a message to service to initiate some longer-running
processing and require a notification back from service in order to
confirm that the requested process has been completed.
6. What is DataContractSerializer and How its different from XmlSerializer?
Serialization is the process of converting an object instance to a
portable and transferable format. So, whenever we are talking about web services, serialization is very important.
Windows Communication Foundation has DataContractSerializer that
is new in .NET 3.0 and uses opt-in approach as compared to XmlSerializer
that uses opt-out. Opt-in means specify whatever we want to serialize
while Opt-out means you don’t have to specify each and every property to
serialize, specify only those you don’t want to serialize.
DataContractSerializer is about 10% faster than XmlSerializer but it has
almost no control over how the object will be serialized. If we wanted
to have more control over how object should be serialized that
XmlSerializer is a better choice.
7. How we can use MessageContract partially with DataContract for a service operation in WCF?
MessageContract must be used all or none. If we are using
MessageContract into an operation signature, then we must use
MessageContract as the only parameter type and as the return type of the
operation.
8. Which standard binding could be used for a service that was designed to replace an existing ASMX web service?
The basicHttpBinding standard binding is designed to expose a service as
if it is an ASMX/ASP.NET web service. This will enable us to support
existing clients as applications are upgrade to WCF.
9. Please explain briefly different Instance Modes in WCF?
WCF will bind an incoming message request to a particular service instance, so the available modes are:
- Per Call: instance created for each call, most efficient in term of memory but need to maintain session.
- Per Session: Instance created for a complete session of a user. Session is maintained.
- Single: Only one instance created for all clients/users and shared among all.Least efficient in terms of memory.
10. Please explain different modes of security in WCF? Or Explain the difference between Transport and Message Level Security.
In Windows Communication Foundation, we can configure to use security at different levels
a. Transport Level security means providing
security at the transport layer itself. When dealing with security at
Transport level, we are concerned about integrity, privacy and
authentication of message as it travels along the physical wire. It
depends on the binding being used that how WCF makes it secure because
most of the bindings have built-in security.
<netTcpBinding>
<binding name="netTcpTransportBinding">
<security mode="Transport">
<Transport clientCredentialType="Windows" />
</security>
</binding>
</netTcpBinding>
b. Message Level Security
For Tranport level security, we actually ensure the transport that is
being used should be secured but in message level security, we actually
secure the message. We encrypt the message before transporting it.
<wsHttpBinding>
<binding name="wsHttpMessageBinding">
<security mode="Message">
<Message clientCredentialType="UserName" />
</security>
</binding>
</wsHttpBinding>
It totally depends upon the requirements but we can use a mixed security mode also as follows:
<basicHttpBinding>
<binding name="basicHttp">
<security mode="TransportWithMessageCredential">
<Transport />
<Message clientCredentialType="UserName" />
</security>
</binding>
</basicHttpBinding>
Q.What is WCF?
Microsoft refers WCF as a programming platform that is used to build
Service-oriented applications. Windows Communication Foundation is
basically a unified programming model for developing, configuring and
deploying distributed services. Microsoft has unified all its existing
distributed application technologies (e.g. MS Enterprise Services, ASMX
web services, MSMQ, .NET Remoting etc) at one platform i.e. WCF. Code
name for WCF was Indigo.
Q.Why to use WCF? or What are the advantages for using WCF?
Service Orientation is one of the key advantages of WCF.
We can easily build service-oriented applications using WCF.
- If compared with ASMX web services, WCF service provides reliability and security with simplicity.
- As oppose to .NET Remoting, WCF services are interoperable.
- Different clients can interact with same service using different communication mechanism. This is achieved by using service endpoints. A single WCF service can have multiple endpoints. So, developer will write code for service once and just by changing configuration (defining another service endpoint), it will be available for other clients as well.
- Extensibility is another key advantage of WCF. We can easily customize a service behavior if required.
Q.What are the core components of WCF Service?
A WCF service has at least following core components.
- Service Class: A ervice class implementing in any CLR-based language and expose at least one method.
- Hosting Environment: a managed process for running service.
- Endpoint: a client uses it to communicate with service.
Q.What is the difference between WCF and ASMX Web services?
The basic difference is that ASMX web service is designed to send and
receive messages using SOAP over HTTP only. While WCF service can
exchange messages using any format (SOAP is default) over any transport
protocol (HTTP, TCP/IP, MSMQ, Named Pipes etc).
You can find detailed discussion on WCF Vs ASMX Web services here.
Q.What are the Endpoints in WCF? or Explain ABCs of endpoint?
For WCF services to be consumed, it’s necessary that it must be exposed; Clients need information about service to communicate with it. This is where service endpoints play their role.
A service endpoint has three basic elements or also called ABCs of an endpoint i.e. Address, Binding and Contract.
Address: It defines “WHERE”. Address is the URL that identifies the location of the service.
Binding: It defines “HOW”. Binding defines how the service can be accessed.
Contract: It defines “WHAT”. Contract identifies what is exposed by the service.
Q.What is a WCF Binding? How many different types of bindings available in WCF?
Bindings in WCF actually defines that how to communicate with the service. Binding specifies that what communication protocol as well as encoding method will be used. Optionally, binding can specify other important factors like transactions, reliable sessions and security.
Another WCF Tutorial gives more detailed understanding of Binding concept in WCF.
There are different built-in bindings available in WCF, each designed to fulfill some specific need.
For WCF services to be consumed, it’s necessary that it must be exposed; Clients need information about service to communicate with it. This is where service endpoints play their role.
A service endpoint has three basic elements or also called ABCs of an endpoint i.e. Address, Binding and Contract.
Address: It defines “WHERE”. Address is the URL that identifies the location of the service.
Binding: It defines “HOW”. Binding defines how the service can be accessed.
Contract: It defines “WHAT”. Contract identifies what is exposed by the service.
Q.What is a WCF Binding? How many different types of bindings available in WCF?
Bindings in WCF actually defines that how to communicate with the service. Binding specifies that what communication protocol as well as encoding method will be used. Optionally, binding can specify other important factors like transactions, reliable sessions and security.
Another WCF Tutorial gives more detailed understanding of Binding concept in WCF.
There are different built-in bindings available in WCF, each designed to fulfill some specific need.
- basicHttpBinding
- wsHttpBinding
- netNamedPipeBinding
- netTcpBinding
- netPeerTcpBinding
- netmsmqBinding
For details on different binding types, please follow the link to WCF bindings.
Q.Can we have multiple endpoints for different binding types in order to serve different types of clients?
Yes, we can have multiple endpoints for different binding types. For
example, an endpoint with wsHttpBinding and another one with
netTcpBinging.
Q.What are the hosting options for WCF Services? Explain.
For a service to host, we need at least a managed process, a ServiceHost
instance and an Endpoint configured. Possible approaches for hosting a
service are:
1. Hosting in a Managed Application/ Self Hosting
a. Console Application
b. Windows Application
c. Windows Service
2. Hosting on Web Server
a. IIS 6.0 (ASP.NET Application supports only HTTP)
b. Windows Process Activation Service (WAS) i.e. IIS 7.0
1. Hosting in a Managed Application/ Self Hosting
a. Console Application
b. Windows Application
c. Windows Service
2. Hosting on Web Server
a. IIS 6.0 (ASP.NET Application supports only HTTP)
b. Windows Process Activation Service (WAS) i.e. IIS 7.0
supports HTTP, TCP,NamedPipes, MSMQ.
Q.What are Contracts in WCF?
A Contract is basically an agreement between the two parties i.e.
Service and Client. In WCF, Contracts can be categorized as behavioral
or structural.
- Behavioral Contracts define that what operations client can perform on a service.
- ServiceContract attribute is used to mark a type as Service contract that contains operations.
- OperationContract attributes is used to mark the operations that will be exposed.
- Fault Contract defines what errors are raised by the service being exposed.
- Structural Contracts
- DataContract attribute define types that will be moved between the parties.
- MessageContract attribute define the structure of SOAP message.
Q.What Message Exchange Patterns supported by WCF?
- Request/Response
- One Way
- Duplex
Request/Response
It’s the default pattern. In this pattern, a response message will always be generated to consumer when the operation is called, even with the void return type. In this scenario, response will have empty SOAP body.
It’s the default pattern. In this pattern, a response message will always be generated to consumer when the operation is called, even with the void return type. In this scenario, response will have empty SOAP body.
One Way
In some cases, we are interested to send a message to service in order to execute certain business functionality but not interested in receiving anything back. OneWay MEP will work in such scenarios.If we want queued message delivery, OneWay is the only available option.
In some cases, we are interested to send a message to service in order to execute certain business functionality but not interested in receiving anything back. OneWay MEP will work in such scenarios.If we want queued message delivery, OneWay is the only available option.
Duplex
The Duplex MEP is basically a two-way message channel. In some cases, we want to send a message to service to initiate some longer-running processing and require a notification back from service in order to confirm that the requested process has been completed.
The Duplex MEP is basically a two-way message channel. In some cases, we want to send a message to service to initiate some longer-running processing and require a notification back from service in order to confirm that the requested process has been completed.
Q.What are the different ways to expose WCF Metadata?
By default, WCF doesn’t expose metadata. We can expose it by choosing one of the following ways:
1. In configuration file, by enabling metadata exchange as follows:
<system.serviceModel>
<services>
<service name="MyService.Service1"
behaviorConfiguration="MyService.Service1">
<endpoint address="" binding="wsHttpBinding"
contract="MyService.IService1">
<identity>
<dns value="localhost"/>
</identity>
</endpoint>
<endpoint address="mex" binding="mexHttpBinding"
contract="IMetadataExchange"/>
</service>
</services>
<behaviors>
<serviceBehaviors>
<behavior name="MyService.Service1">
<serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled="true"/>
<serviceDebug includeExceptionDetailInFaults="false"/>
</behavior>
</serviceBehaviors>
</behaviors>
</system.serviceModel>
2. ServiceHost can expose a metadata exchange endpoint to access metadata at runtime.
using (ServiceHost host = new ServiceHost(typeof(MyService)))
{
ServiceMetadataBehavior behavior = new ServiceMetadataBehavior();
behavior.HttpGetEnabled = true;
host.Description.Behaviors.Add(behavior);
host.Open();
Console.WriteLine("My Service here..........");
Console.ReadLine();
host.Close();
}
Q.What is mexHttpBinding in WCF?
In order to generate proxy, we need service metadata and mexHttpBinding returns service metadata.
If we look into our configuration file, service will have an endpoint with mexHttpBinding as follows:
<endpoint address="mex" binding="mexHttpBinding" contract="IMetadataExchange"/>
and service metadata behavior will be configured as follows:
<serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled="true"/>
Before deployment of application to production machine, it should be disabled.
In order to support other protocols, related bindings are mexHttpBinding, mexHttpsBinding, mexTcpBinding.
Q.What is a Service Proxy in Windows Communication Foundation?
A service proxy or simply proxy in WCF enables application(s) to
interact with WCF Service by sending and receiving messages. It’s
basically a class that encapsulates service details i.e. service path,
service implementation technology, platform and communication protocol
etc. It contains all the methods of service contract (signature only,
not the implementation). So, when the application interact the service
through proxy, it gives the impression that it’s communicating a local
object.
We can create proxy for a service by using Visual Studio or SvcUtil.exe.
Q.What are the different ways to generate proxy in WCF?
Generating proxy using Visual Studio is simple and straight forward.
i) Right click References and choose “Add Service Reference”.
ii) Provide base address of the service on “Add Service Reference” dialog box and click “Go”
button. Service will be listed below.
iii) Provide namespace and click OK.
Visual studio will generate a proxy automatically.
We can generate proxy using svcutil.exe utility using command line. This
utility requires few parameters like HTTP-GET address or the metadata
exchange endpoint address and a proxy filename i.e. optional.
svcutil http://localhost/MyService/Service1.svc /out:MyServiceProxy.cs
If we are hosting the service at a different port(other than default for
IIS which is 80), we need to provide port number in base address.
svcutil http://localhost:8080/MyService/Service1.svc /out:MyServiceProxy.cs
For parameter details regarding svcutil, please follow the MSDN link
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa347733.aspx
Q.Difference between using ChannelFactory and Proxies in WCF?
A ChannelFactory creates a kind of Channel used by clients to communicate with service endpoints.
If we have control over Server and Client, then ChannelFactory is a good
option because it relies on having local interfaces that actually
describes the service i.e. service contract.
On the other hand, If we don’t have control over server and only have
WSDL/URL, then it’s better to generate proxy using Visual Studio or
SvcUtil.
SvcUtil is better option as compared to Visual Studio because we have more control in case of SvcUtil.
Q.How to create proxy for Non-WCF Services?
In case of Non-WCF Services, we can create proxy by either using Visual
Studio or svcUtil.exe tool by pointing to WSDL of the non-WCF service.
In this scenario, we can’t create proxy through ChannelFactory or
manually developing proxy class because we don’t have local interfaces
i.e. service contract.
Q.Breifly explain Automatic Activation in WCF?
Automatic activation means service starts and serves the request when a
message request is received, but service doesn’t need to be running in
advance.
There are few scenarios in which service needs to be running in advance, For example, in case of Self-Hosting.
Q.What are the different WCF Instance Activation Methods available?
WCF supports three different types of Instance Activation methods:
a) Per Call.
b) Per Session.
c) Singleton.
For details on WCF Instance Activation Methods, please refer other article “WCF Interview Questions”.
Q.What are the different ways to handle concurrency in WCF?
There are three different ways to handle concurrency in WCF that are:
a) Single.
b) Multiple.
c) Reentrant.
Single: means at a given time, only a single request can be
processed by WCF service instance. Other requests will be waiting until
the first one is fully served.
Multiple: means multiple requests can be served by multiple threads of a single WCF service instance.
Reentrant: means a single WCF service instance can process one
request at a given time but the thread can exit the service to call
another service.
We can apply these concurrency settings by putting ConcurrencyMode property in ServiceBehavior as follows:
[ServiceBehavior(ConcurrencyMode = ConcurrencyMode.Multiple]
Public class MyService : IMyService
{
}
Q.What is WCF throttling?
WCF throttling enables us to regulate the maximum number of WCF
instances, concurrent calls and concurrent sessions. Basic purpose is to
control our WCF service performance by using Service throttling
behavior.
In configuration file we can set this behavior as follows:
<serviceBehavior>
<behavior name=”MyServiceBehavior”>
<serviceThrottling
maxConcurrentInstances=”2147483647”
maxConcurrentCalls="16"
maxConcurrentSessions="10"
</behavior>
</serviceBehavior>
Above given values are the default ones, but we can update it after looking into
the requirements of our application.